Heart disease is a pervasive health issue worldwide, affecting millions of people each year. Two common surgical procedures used to treat coronary heart disease are angioplasty and bypass surgery. While both aim to improve blood flow to the heart, they differ significantly in their approach, procedure, and recovery. In this blog, we’ll explore the differences between heart angioplasty and bypass surgery to help you understand which might be the right option for your specific heart condition.
Heart Angioplasty – Differences Between Heart Angioplasty and Bypass Surgery
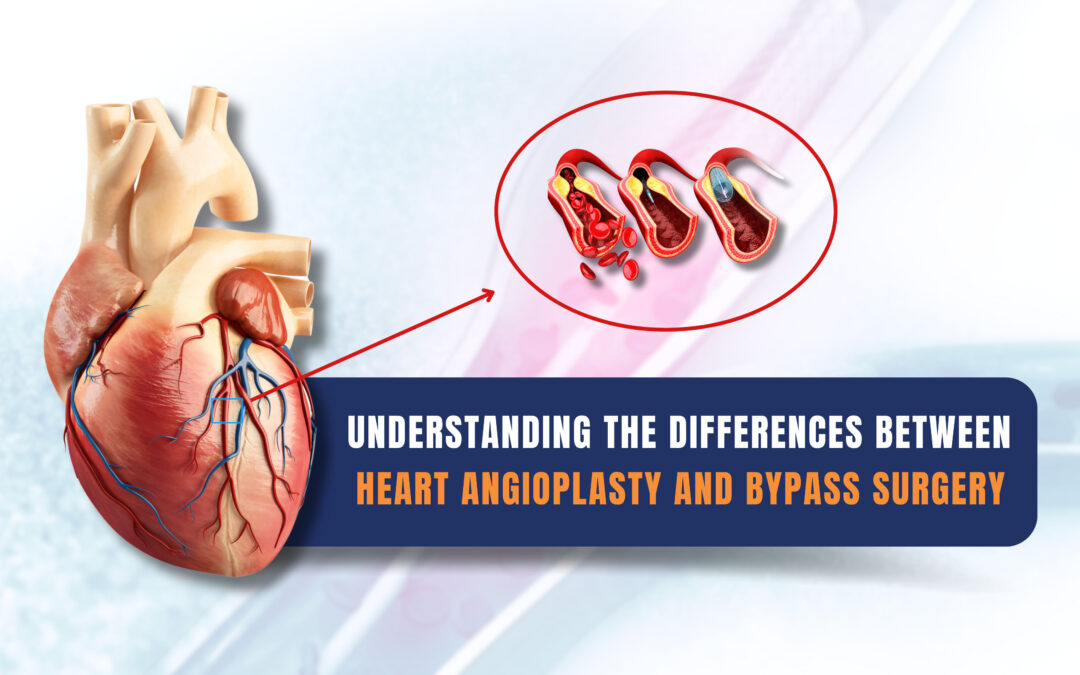
- Procedure: Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive procedure. It involves threading a thin catheter through an artery, usually in the groin or wrist, to the site of the blocked coronary artery.
- Purpose: Angioplasty is primarily used to treat narrowed or blocked arteries (atherosclerosis). During the procedure, a balloon attached to the catheter is inflated to compress the plaque against the artery walls, widening the vessel and restoring blood flow.
- Stenting: A stent (a small, mesh-like tube) is inserted into the treated artery to help keep it open. Drug-eluting stents are often used to prevent re-narrowing of the artery.
- Anesthesia: Angioplasty is typically performed under local anesthesia, and patients usually remain awake during the procedure.
- Recovery: Recovery time for angioplasty is relatively short. Most patients can go home the same day or within a day or two. Full recovery may take a week or two, depending on individual factors.
- Risks: While generally considered safe, angioplasty carries some risks, including bleeding, infection, blood vessel damage, and the possibility of restenosis (re-narrowing of the artery).
Heart Bypass Surgery
- Procedure: Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), commonly known as bypass surgery, is an open-heart procedure. It involves creating a new pathway for blood to bypass blocked or narrowed arteries. Surgeons use a healthy blood vessel (usually from the leg or chest) to create the bypass.
- Purpose: Bypass surgery is typically recommended when multiple coronary arteries are severely blocked or when angioplasty is not suitable due to complex coronary anatomy.
- Number of Arteries: Bypass surgery can involve multiple grafts, addressing blockages in several arteries simultaneously.
- Anesthesia: Bypass surgery is performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is unconscious during the procedure.
- Recovery: The recovery period for bypass surgery is longer and more intensive than angioplasty. Patients often spend several days in the hospital and may need several weeks to months for a full recovery.
- Risks: While bypass surgery carries higher risks than angioplasty due to its invasiveness, it is a well-established and safe procedure. Risks include infection, bleeding, heart rhythm problems, and complications related to the use of the heart-lung machine during surgery.
Choosing the Right Option
The choice between angioplasty and bypass surgery depends on various factors, including the extent and location of blockages, the patient’s overall health, and the preferences of both the patient and the healthcare team. Here are some considerations:
- Number and Severity of Blockages: Angioplasty is often suitable for single or limited blockages, while bypass surgery is preferred for multiple or complex blockages.
- Overall Health: Patients with other health issues may not be good candidates for surgery and may opt for angioplasty as a less invasive option.
- Long-Term Goals: Bypass surgery tends to provide more durable results for severe coronary artery disease, while angioplasty may require repeat procedures over time.
- Patient Preference: Some patients may have strong preferences for one procedure over the other, which should be taken into account.
- Medical Team Recommendation: The expertise and recommendations of the medical team, including cardiologists and surgeons, play a crucial role in the decision-making process.
Conclusion
Both angioplasty and bypass surgery are essential tools in the treatment of coronary heart disease. Understanding the differences between heart angioplasty and bypass surgery is crucial for making an informed decision about which approach is best suited to your specific condition. Ultimately, the goal of both procedures is to restore blood flow to the heart muscle and improve overall heart health, leading to a better quality of life for individuals with coronary artery disease. Always consult with your healthcare team to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your unique situation.